Google Algorithms
- Home
- Google Algorithms
Evolution of Google Algorithms since 1998
Google Algorithms
The Evolution of Google Algorithms
From the Beginning to Modern Changes
With the upcoming changes in Google’s search engine algorithms, it’s interesting to take a look back at how these algorithms have changed since Google first started back in 1998. By understanding where Google came from, we can see how the company has been working to improve search results and make social media more important in how they rank things in search results. Here’s a rundown of some of the important moments in Google’s algorithm history as we get ready for the new changes. It’s clear from looking at this history that the changes have happened in bursts, but they’ve all been aimed at specific goals. I’ll keep updating this page as Google announces new algorithm changes on their website.

The Birth of Google Algorithms
Google introduced its search engine in 1998, marking the start of its journey.
The Introduction of PageRank Algorithm (2000)
In the year 2000, Google launched the PageRank algorithm. This was a big change from how search results were ranked before, although the exact details of how it worked weren’t fully explained. In September of that year, Google made some significant adjustments to the PageRank system, but they didn’t reveal exactly what those changes were.
The Turbulent Year of 2002
September 2002 was a pivotal moment for Google’s algorithms. An important update caused quite a stir. Unexpectedly, some search results started showing 404 error pages in the top 10 results. This was also the first time that the PageRank system faced a major setback, leading to its temporary demise.
As we follow the timeline of Google’s algorithm changes, we can see a pattern of evolution with significant moments that have shaped its course. These changes haven’t always been gradual; sometimes, they’ve caused disruptions that led to unexpected outcomes.
Google Algorithms – the Changing Landscape
Google’s journey in refining its algorithms has been driven by two main objectives: reducing irrelevant search results and giving more weight to social media in determining search rankings.
Over the years, Google has been committed to making sure that search results are as relevant as possible to users’ queries. Despite the ongoing challenge of irrelevant results, Google has been working steadily to ensure that users get the information they’re looking for.
At the same time, the importance of social media in SEO (Search Engine Optimization) has become more evident. Google has recognized that social media interactions, like shares and reactions, can indicate the credibility and relevance of content. This recognition has led Google to include social media metrics in its algorithms, boosting the visibility of content that gains traction on social platforms.
Google Algorithms- Anticipating Algorithmic Changes As we stand at the edge of the future, ready for new algorithm changes, it’s clear that Google’s journey with algorithms is ongoing. The continuous evolution, driven by a commitment to providing the best user experience, keeps pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the digital world.
Each Google algorithm update contributes to a more refined and accurate search experience, aligning search results more closely with what users are actually looking for. The dynamic nature of these updates reflects Google’s ability to adapt to the ever-changing digital landscape.
Tracing Google algorithms from its beginnings in 1998 to the brink of the latest changes reveals an ongoing process of transformation. The consistent themes of improving relevance and integrating social media highlight Google’s overarching goals. As the digital landscape expands and algorithm updates become a regular occurrence, Google remains dedicated to creating an information environment that is both informative and engaging, perfectly attuned to the evolving needs of its users.
Google launched its search engine in March of this year.
September 2002 – Google’s update causes uproar. 404 pages show up in the top 10 search results, pagerank dies an early death for the first time.
Google Algorithms: The Google Dance 2003
Early 2003- Google swing widely then settle. By the time Cassandra, Dominic and Esmeralda updates are done, Google has outranked multiple linking from self owned sites and the same C class Ips. SEOS start thinking maybe page tiles and link text matter.
In February, Google announced at the SES Boston that they were using algorithm combinations to refresh their monthly index which some people coined as “The Google Dance”. In April, the “Cassandra” update helped to eliminate hidden links and hidden texts from being counted. By May, the “Dominic” update changed how back-links were counted. The “Google Dance” ended in July with the index being updated on a daily basis.
November 2003 – Florida update caused high ranking sites got outranked.
Relevance drops and connections are as solid as baby Swiss cheese. In November, Google made major progress against keyword stuffing in their “Florida” update.
Austin, Brandy and LSI updates 2004
2004: Google started the year in January with the “Austin” update which may have included updates to their algorithms. They did continue their assault on On-Page tactics like keyword stuffing and invisible text. The next month the “Brandy” update added Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) which changed keyword analysis.
Nofollow attributes and Sitemaps 2005
2005: Again in January, Google agreed with Microsoft and Yahoo with “nofollow” link attribution to clean out spam. In June, HTML sitemaps change with XML sitemaps which gave SEO the ability to influence indexation and crawling. From the end of 2005 until 2009 there were no major changes, although there were some significant developments in how Google algorithms changes subtly over this time period.
Vincent algorithm 2009
2009: February marked the arrival of the “Vincent” update which seemed to favor big brand websites, though this was denied. In August, Google previewed the massive changes to their infrastructure and in December Google News, Twitter and other feeds were integrated into the system.
Ecommerce reviews 2010
2010: In December, an e-commerce site was reviewed to have search rankings based on negative reviews. This altered the algorithms in this area. Social media sites gained even more prominence as well.
In this year Negative SEO was born. I have been fighting with this issue since then.My own website went under attack of many negative SEO and DDos attacks.

Panda Farmer and G+ launched 2011
2011: In February, a huge update with the arrival of Panda Farmer in Google algorithms occurred which affected over 10% of search results, this update hit Europe in April with similar effects. By March, Google had placed their “+1” button which helped influence both organic and paid search results, this was a direct response to Facebook and Twitter. Panda was in turn updated through the year, but in June Google launched their own social media which accumulated over 10 million users in just two weeks.
Search + your world and implementing of social data into Serp 2012
2012: Search + Your World was launched in January, incorporating user profiles and social data into SERP.
Search + your world and implementing of social data into Serp 2012
2012: Search + Your World was launched in January, incorporating user profiles and social data into SERP.
Google Algorithms in 2013
Google Penguin 2.0
Google Algorithm in 2013 This is the next generation of the Penguin algorithm. Release Date: Penguin 2.0 was officially rolled out on May 22, 2013.
Focus on Link Quality: The primary objective of Penguin updates, including version 2.0, was to target websites with low-quality or spammy backlinks. Google aimed to reward websites with high-quality, natural links and penalize those involved in manipulative link-building practices.
Devaluing Manipulative Links: Penguin 2.0 specifically sought to devalue not just the individual spammy links but also the entire value of the linking website. This was intended to discourage webmasters from relying on unnatural and manipulative link-building strategies.
Impact on Rankings: Websites that were found to be in violation of Google’s guidelines and had a significant number of low-quality backlinks could experience a drop in their search engine rankings.
Algorithmic Penalty: Penguin updates, including version 2.0, are algorithmic penalties, meaning they are applied automatically by Google’s algorithms rather than being manually imposed by human reviewers.
Hummingbird Algorithm
 Hummingbird algorithm focuses on parsing searches as complex questions. It works like Facebook graph search and replies to ambiguous queries such as what is my friends’ favorite restaurant. Google Hummingbird represents a shift towards more sophisticated and context-aware search algorithms, aiming to provide users with more relevant and accurate results by understanding the meaning behind their queries.
Hummingbird algorithm focuses on parsing searches as complex questions. It works like Facebook graph search and replies to ambiguous queries such as what is my friends’ favorite restaurant. Google Hummingbird represents a shift towards more sophisticated and context-aware search algorithms, aiming to provide users with more relevant and accurate results by understanding the meaning behind their queries.
Google algorithm hummingbird’s characteristics:
Semantic Search:
Hummingbird is designed to understand the meaning behind search queries, focusing on the intent of the user rather than just matching keywords.
It incorporates semantic search technology, which helps Google better interpret the context and relationships between words in a query.
Conversational Search:
With the rise of voice search and more natural language queries, Hummingbird is optimized to handle conversational search queries.
It considers the entire query rather than individual keywords, making it more effective in understanding the user’s intent.
User Intent:
The algorithm aims to deliver search results that align with the user’s intent, providing more accurate and relevant information.
It takes into account the context of the query, user location, and personalized search history to deliver tailored results.
Long-Tail Keywords:
Hummingbird is adept at understanding long-tail keywords, which are longer and more specific phrases that users might type into the search bar.
This allows for more precise results and a better match between user queries and content.
Mobile-Friendly:
In line with the increasing use of mobile devices for search, Hummingbird is designed to prioritize mobile-friendly websites and responsive design.
Knowledge Graph Integration:
The Hummingbird algorithm integrates with Google’s Knowledge Graph, a database of interconnected information about people, places, and things.
This integration enhances the ability to provide direct answers to queries and improve the overall search experience.
Penguin Update 5 October 04, 2013 Penguin 2.1 (Penguin 5th edition)
This was released in Google’s continuing battle against web spam. We see a corresponding spike in the Rank Risk Index on October 5th.
Undisclosed Activity November 15, 2013
There are a lot of chatter in the various webmaster and SEO forums and blogs about SERP changes, but no official announcement from Google.
Authorship Rich Snippet Update December 18, 2013
In what may be the most dramatic Google update of 2013, Authorship & Rich Snippet results dropped as much as 15% as Google tightened the qualifications for rich snippets. Authors reported problems and were advised to refer to Google’s rel=”author” FAQs to ensure they’re following the rules.
Top Heavy 3 Update in 2014
February 06, 2014 Google’s Page Layout Algorithm targets pages with disproportionate number of ads above the fold in relation to page content. Google’s Matt Cutts confirmed this algorithm refresh in a Tweet. Page Layout Algorithm goal is to make users’ search experience more efficient and quick, enabling them to reach the content they’re seeking.
Undisclosed Activity
March 24, 2014 Webmaster and SEO forum rumors of a Soft Panda update around March 24th match up with the red zone dates displaying in our Rank Risk Index, however, no official announcement has been made by Google.
Algorithm Activity – Undisclosed
April 18, 2014 The Rank Risk Index has been indicating volatile activity by Google for much of April. Lots of chatter in the various webmaster and SEO forums and blogs about dramatic SERP changes, but no official announcement from Google.
Payday Loan Algorithm 2.0
May 18, 2014 Google announced the release of an update to their Spam Algorithm that targets the type of queries that return an excessive number of spammy results. This specific update was an international roll out that is reported to affect different languages to different degrees and noticeably impacts English queries by about 0.2%. Matt Cutts Tweeted: “This past weekend we started rolling out a ranking update for very spammy queries.” Search Engine Watch reported “Over the weekend we began rolling out a new algorithmic update,” a Google spokesperson told SEW. “The update was neither Panda nor Penguin – it was the next generation of an algorithm that originally rolled out last summer for very spammy queries.”

Panda 4.0
May 20, 2014 Our Rank Risk Index has been showing sharp fluctuations in recent weeks causing lots of chatter in SEO and webmaster forums. By mid-May we started to see a relative calm, but suddenly the red alert went up again and shortly after that Matt Cutts announced on Twitter that Google had launched Panda 4.0 and plans to be rolling out more updates. The goal of Panda has been to penalize poor content quality and scraper sites, while boosting sites with great content up in the SERPs and thereby providing Google users with high quality results. Google’s Matt Cutts announced Panda 4.0 on Twitter.
Payday Loan Algorithm 3.0
June 12, 2014 Google rolled out an update to their PayDay Loan Spam Algorithm. Version 3.0 targets the queries for ‘payday loans’, ‘casinos’, ‘accident claims’ and a variety of others that return an excessive number of web spam results. Google’s Matt Cutts announced this algorithm update on Twitter.
Google Local Algorithm Update
July 24, 2014 Google launched an update to their local search algorithm to help them provide more accurate and relevant local search results. The chat in the Webmaster World Local Search Forum suggests that the update was causing inconsistent results, with “major flux” still occurring a week after the rollout. Small Business Trends provides an analysis of how this update affects local businesses.
September 20, 2014
A new Panda algorithm is rolled out. Matt Cuts confirmed in a message on G+ about this update. Based on user (and webmaster!) feedback, Google’s engineers have been able to discover a few more signals to help Panda identify low-quality content more precisely. This results in a greater diversity of high-quality small- and medium-sized sites ranking higher.Depending on the locale, around 3-5% of queries are affected.
Google Algorithm Update: mobile friendliness
April 21, 2015 The algorithm scans each page on the site, checking for load times, responsive design elements, and mobile best practice. For now searches on tablets won’t be affected.
Google Algorithm Refresh Panda 4.2
July 21, 2015
Panda refresh has affected about 2%-3% of English language queries, which is relatively small compared to the past updates.
Google RankBrain
October 25, 2015
RankBrain is the first system within Google’s search algorithm to employ machine learning to process huge volumes of search queries submitted to Google, including voice search. It attempts to understand what those queries mean and use that understanding to provide better answer
The Impact Of Google RankBrain on Digital Marketing
User intent is the key focus of algorithm changes in 2016
Google Possum Algorithm
September 1st, 2016
 It was launched on September first 2016 and impacts the local search results mainly directory listing. It catches spam directory listings on the local search results such as Google Maps, Google Places and Map Pack.
It was launched on September first 2016 and impacts the local search results mainly directory listing. It catches spam directory listings on the local search results such as Google Maps, Google Places and Map Pack.
Google Algorithms in 2017
A new update of Google Penguin
January 10, 2017
This algorithm penalizes websites which have pop-ups that block content, especially on mobile devices. Google encourages simple and easy to use access to content on mobile and if your website has pop-up which blocks the content, Google algorithm will penalize it.
Note:Those who follow me on social media have seen my warnings about not using too many pop-ups. There you have it, Google updated Penguin algorithm to stop annoying pop-ups. I have seen 99% of SEOs and marketers use pop-ups in the middle of their content pages to capture leads. They write lies about how these annoying content blocking elements generate leads for them. Well, they don’t. I click away from websites with annoying pop-ups. If you use it don’t put it in the middle of your website to block content. It annoys visitors. Your websites get penalized by Google.
Fred Algorithm
Fred algorithm March , 2017
Fred Algorithm puts a higher emphasis on link quality. This algorithm has a focus on low value content, Private Blog Networks with low quality back links and content which are generated to earn revenue via Google Adsense and affiliate ads.
Read: How to Supercharge Your Private Blog Network PBN

Google Algorithm changes in 2018
Google Medic
Google algorithm change which impacted news, scientific, medical, financial websites and all websites that allow transactions (e-commerce).The update of the guidelines regarded the insertion of specific indications on the YMYL pages, in the medical and non-medical fields. Based on Google’s announcement the three factors are the following:
– The Expertise of the content creator;
-The Authoritativeness of content creator, of the content itself and of the website;
– The Trustworthiness of content creator, of the content itself and of the website.
Google Maccabees Update
It targets keyword permutations on different pages. Many travel, real estate, e-commerce and affiliate websites lost ranking in December 2017 due to this algorithm update.
Google Bert Algorithm
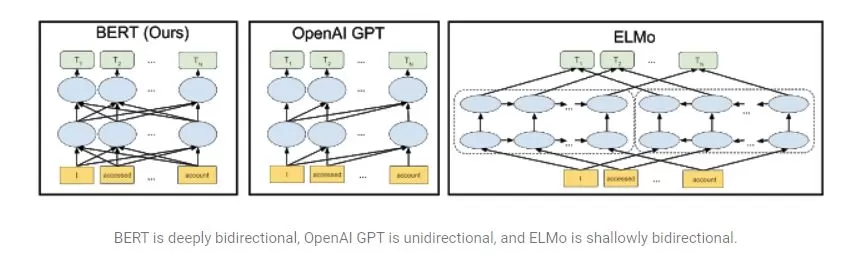
BERT algorithm — Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers — leverages machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) to better understand the context of a search query. While Bing had already been using BERT, Google announced it use this algorithm for some searches in the U.S. BERT builds upon recent work in pre-training contextual representations — including Semi-supervised Sequence Learning, Generative Pre-Training, ELMo, and ULMFit. Google used the straightforward technique of masking out some of the words in the input and then condition each word bidirectionally to predict the masked words.Example: The man went to the store. He bought a gallon of milk. Mask words are store and gallon. NLP researchers who use BERT will never need to pre-train their own models from scratch. The BERT models that Google released are English-only, but Google hopes to release models which have been pre-trained on a variety of languages in the near future. The source of illustration below is from Google.
September 2019 Core Update
 Google has announced that they have released a broad core algorithm update on the 24th of September 2019 called “September 2019 Core Update”. Google gave some guidance at the beginning of August about what webmasters should know about Google’s core updates. One of the updates is that those who implemented review snippet on their websites, their review ranking won’t show in search results anymore. Google reevaluates content on websites and their ranking. Based on one’s observation, websites with content from high authority sites pointing to them, will rank higher in search result for their keywords. There is nothing new about it, but the difference is that Google A.I recognizes artificial content manipulation.
Google has announced that they have released a broad core algorithm update on the 24th of September 2019 called “September 2019 Core Update”. Google gave some guidance at the beginning of August about what webmasters should know about Google’s core updates. One of the updates is that those who implemented review snippet on their websites, their review ranking won’t show in search results anymore. Google reevaluates content on websites and their ranking. Based on one’s observation, websites with content from high authority sites pointing to them, will rank higher in search result for their keywords. There is nothing new about it, but the difference is that Google A.I recognizes artificial content manipulation.
Google update 2020 ( E.A.T)
The Google algorithm update brought changes to mobile apps and games.
The leading App stores, Google Play, and Apple Store, were huge winners, with a 93% and 45% SERP ranking improvement respectively.
In May 2020 Google’s core update completed. It was about a strong E-A-T. That stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness. Reading Google guidelines may help you assess how your content is doing from an E-A-T perspective and improvements to consider. Long story short improve your backlink building and getting more social media engagement in order to increase the authority of your websites. All these algorithms are in favor of quality content and website authority.
December 2020 Google Core Web Vital Algorithm
Google Algorithm in 2021
Core Web Vitals algorithm update happened in May 2021, the impact that we have all currently been seeing, given that Web Vitals should be technically inert.
Google take into consideration three important ‘Core Web Vitals’ metrics such as: page loading, page responsiveness, and page visual stability. Google search engine measures each of them for pages on a website and gives a status of ‘Poor’, ‘Needs improvement’ or ‘Good’
Read more here: the impact of Google Vitals Core Algorithm on SEO

Google June 2021 Core Update Roll Out
Google rollout the first broad core update of 2021 – June 2021 Core Update. A common question after a core update is how long does it take for a site to recover, if it improves content?
Broad core updates tend to happen every few months. Content that was impacted by one might not recover—assuming improvements have been made—until the next broad core update is released.
However, Google is constantly making updates to their search algorithms, including smaller core updates. They don’t announce all of these because they’re generally not widely noticeable. Still, when released, they can cause content to recover if improvements warrant.
Do keep in mind that improvements made by site owners aren’t a guarantee of recovery, nor do pages have any static or guaranteed position in our search results. If there’s more deserving content, that will continue to rank well with our systems. Google also announced the second batch of Google Spam Update on June 28th and the implications of it remain the same as the earlier one.
November 2021 Core Update
 It focuses on ranking websites that are offering better quality content for the search queries entered by the users. The broad core update doesn’t mean there is something wrong with your website. If you see a drop in your website’s rankings it means you need to update your content.
It focuses on ranking websites that are offering better quality content for the search queries entered by the users. The broad core update doesn’t mean there is something wrong with your website. If you see a drop in your website’s rankings it means you need to update your content.
Content quality questions:
– Does the content provide original information, reporting, research or analysis?
– Does the content provide a substantial, complete or comprehensive description of the topic?
– Does the content provide insightful analysis or interesting information that is beyond obvious?
– If the content draws on other sources, does it avoid simply copying or rewriting those sources and instead provide substantial additional value and originality?
– Does the headline and/or page title provide a descriptive, helpful summary of the content?
– Does the headline and/or page title avoid being exaggerating or shocking in nature?
– Is this the sort of page you’d want to bookmark, share with a friend, or recommend?
– Would you expect to see this content in or referenced by a printed magazine, encyclopedia or book?
December 2021
Product review Update
Google rolled out the new product review update for websites in English.
The best practices that can be used for a website’s content
1) Adding more multimedia to your product reviews to support your expertise and showcase your authenticity.
2) Providing links to multiple sellers, which will give your readers the option to purchase from the merchant of their choice.
This new update will promote review content better than the templated information available on the web.
Google will be promoting these in-depth product reviews in their rankings.

The Page Experience Update in 2022
Page Experience was designed to improve the user experience on the website. Google algorithm gives score based on the following:
Core Web Vitals: Get the page speed right and fix core web vitals’ issues such as:
CLS, LCP, FID errors. The core web vitals are the subset of web vitals that apply to all web pages.
In google metrics there are the three aspects of the user experience loading, interactivity, and visual stability. In 2021 google updated a new ranking factor core web vitals therefore the optimization of Core web vitals is needed for google ranking.
Mobile usability: A page must be mobile friendly
Security issues: Make sure your website has no security issues including hacking to some pages and so on.
Ad Experience: Use proper ad placements on the site that do not block your content and not annoying.

Google’s Link Spam Update
Do not use bad and irrelevant backlinks and keep an eye on your content. Make sure you publish quality content on your pages.

The Multitask Unified Model (MUM)
The Multitask Unified Model (MUM) uses the power of artificial intelligence to help users complete more complex tasks. It is more powerful than Google Bert Algorithm ( watch my video about Google Bert here:
Mum addresses complex search queries which require an average of eight searches to resolve. MUM understands language and generates it. It’s trained across 75 different languages and many different tasks at once, allowing it to develop a more comprehensive understanding of information and world knowledge than previous models. And MUM is multimodal, so it understands information across text and images and, in the future, can expand to more modalities like video and audio. It is great for multilingual queries and websites.
Google Gemini
What is Google Gemini? Google Gemini is like a super smart computer thing that Google is making. It’s supposed to be fantastic at talking and thinking, even better than other computer talkers. They say it’s gonna be like mixing a super word expert with a game champion. It’s got to be really, really good to be the best! But, it might be tough because people already like another computer talker called ChatGPT. So, Gemini has to be extra special to get people to use it. And it has to be nice and not do bad stuff, and keep learning to get even better. Gemini uses secrets from Google to learn, but it has to be fair and not tell anyone’s secrets. And it should be fun and easy for everyone to use. That’s what Google Gemini is all about! Watch this video.
September 2023 Helpful Content Update
Google has released another update to its helpful content system. The update was released on September 14, 2023, and should take about two weeks to complete. Google mentioned that this update will improve the classifier system it uses to determine the usefulness of content.
Google’s March 2024 core update is bringing a seismic shift to the SEO industry. This major update might sweep the web the same way the Panda and Penguin updates did. Its impact is enormous and widespread.
Google’s November 2024 Core Update, officially known as the November 2024 Core Update
 It began rolling out on November 11, 2024. This update is part of Google’s ongoing efforts to refine its search algorithm, focusing on delivering more relevant, high-quality content. The update prioritizes content that meets user intent over material designed primarily for search rankings. Websites providing original, well-structured, and helpful content are likely to benefit, while those relying on low-quality or manipulative SEO tactics may see declines in visibility.
It began rolling out on November 11, 2024. This update is part of Google’s ongoing efforts to refine its search algorithm, focusing on delivering more relevant, high-quality content. The update prioritizes content that meets user intent over material designed primarily for search rankings. Websites providing original, well-structured, and helpful content are likely to benefit, while those relying on low-quality or manipulative SEO tactics may see declines in visibility.
The December 2024 Google Core Update is a broad adjustment to Google’s search algorithm, aimed at improving the quality and relevance of search results. It affects how websites rank, and creators are encouraged to focus on high-quality, user-centered content. Changes may take up to two weeks to fully reflect.
 Google’s March 2025 update might shake up SEO—could your content make or break your rankings? Google’s March 2025 update prioritizes people-first content, focusing on authenticity, expertise, user experience, and quality over SEO tricks. Read more in my article on Google March 2025 core update
Google’s March 2025 update might shake up SEO—could your content make or break your rankings? Google’s March 2025 update prioritizes people-first content, focusing on authenticity, expertise, user experience, and quality over SEO tricks. Read more in my article on Google March 2025 core update